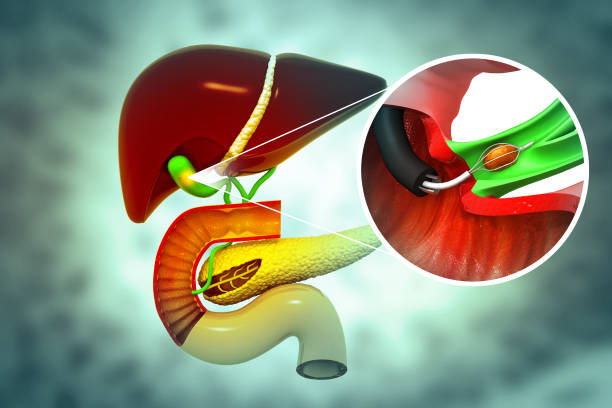
Gallstones removing in the Gallbladder. 3d illustration
Cholecystitis
What is Cholecystitis?
Cholecystitis is the inflammation of the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, which aids in digestion. It can be acute or chronic and is often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct.
Types of Cholecystitis:
- Acute Cholecystitis: Sudden onset of inflammation, often due to gallstones.
- Chronic Cholecystitis: Long-term inflammation that can occur after repeated episodes of acute cholecystitis.
Main Causes of Cholecystitis:
- Gallstones: The most common cause; stones can block the cystic duct, leading to inflammation.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: Tumors or strictures can impede bile flow.
- Infections: Bacterial infections may contribute to inflammation.
- Vascular Compromise: Reduced blood flow to the gallbladder can lead to inflammation.
- Trauma or Surgery: Physical injury or surgical procedures can trigger inflammation.
Signs and Symptoms of Cholecystitis:
- Abdominal Pain: Severe pain in the upper right abdomen that may radiate to the back or right shoulder.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often accompanies abdominal pain.
- Fever: Low-grade fever may be present.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or bloating in the abdomen.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes may occur if bile flow is obstructed.
Risk Factors for Cholecystitis:
- Gallstones: The primary risk factor for developing cholecystitis.
- Obesity: Increased body weight is associated with gallstone formation.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially in people over 40.
- Gender: More common in women, particularly those who are pregnant or on hormone replacement therapy.
- Diet: High-fat and low-fiber diets may contribute to gallstone formation.
How to Prevent Cholecystitis:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting fats can help reduce the risk of gallstones.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Weight loss should be gradual to avoid gallstone formation.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help prevent obesity and gallstones.
- Avoid Rapid Weight Loss: This can increase the risk of gallstone formation.
How Cholecystitis is Diagnosed:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessment of symptoms and risk factors.
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of infection and liver function.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the gallbladder and detect gallstones or inflammation. CT scans may also be employed.
- HIDA Scan: A nuclear medicine test to assess gallbladder function.
Treatment for Cholecystitis:
- Medications: Antibiotics to treat infection, analgesics for pain relief.
- Dietary Changes: Initially, a low-fat diet may be recommended.
- Surgery: Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) is often necessary, especially in acute cases. It can be done laparoscopically (minimally invasive) or through open surgery.
Home Remedies for Cholecystitis:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out toxins.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the abdomen may relieve pain.
- Herbal Teas: Peppermint or ginger tea may help soothe digestive discomfort.
Ayurvedic Medicine for Cholecystitis:
- Triphala: A blend of three fruits known for its digestive benefits and ability to support liver health.
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it may help reduce inflammation.
- Ginger: Can aid digestion and relieve nausea.
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry): Rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, it may support liver function.
Precautions:
- Seek medical attention for severe abdominal pain or symptoms of cholecystitis.
- Follow dietary recommendations and avoid high-fat foods, especially during recovery.
- Monitor for signs of complications, such as jaundice or worsening pain.
Self-Care Tips:
- Keep a symptom diary to identify triggers and patterns.
- Gradually reintroduce foods as tolerated after an acute episode.
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote overall health.
Conclusion:
Cholecystitis is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Managing risk factors and seeking medical care for symptoms can lead to effective treatment and recovery.
Disclaimer:
The information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Additional Tips:
- Stay informed about your condition and treatment options.
- Join support groups for individuals with gallbladder issues for shared experiences and resources.
- Regularly review and adjust your treatment plan with your healthcare team based on symptom changes or new research.