Man face divided into two parts one healthy and one unhealthy. Yellowish eyes and skin. Bad habits vs good habits. Jaundice, liver failure. Risk factors of alcohol drinking. High quality photo
Jaundice is a condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes due to high levels of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. Jaundice is not a disease itself but a symptom of underlying conditions affecting the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas.
Causes:
- Liver Diseases: Conditions like hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer can impair the liver’s ability to process and excrete bilirubin.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Rapid breakdown of red blood cells increases bilirubin levels, leading to jaundice.
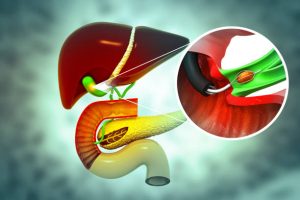
- Obstruction of Bile Ducts: Gallstones, tumors, or inflammation in the bile ducts can block the flow of bile, causing jaundice.
- Newborn Jaundice: Common in newborns due to an immature liver that may not process bilirubin effectively.
- Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and jaundice.
- Viral Infections: Infections such as hepatitis A, B, and C can cause inflammation of the liver, leading to jaundice.
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Gilbert’s syndrome, which affects how the liver processes bilirubin, can result in jaundice.
- Pancreatic or Gallbladder Cancer: Tumors can obstruct the bile ducts, causing jaundice.
Risk Factors:
- Alcohol Use: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage and jaundice.
- Hepatitis: Exposure to hepatitis viruses through contaminated food, water, or needles increases the risk.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like sickle cell anemia or thalassemia that affect red blood cells can lead to jaundice.
- Newborns: Infants, especially premature babies, are more susceptible to jaundice due to immature liver function.
- Gallstones: A history of gallstones increases the likelihood of bile duct obstruction.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of fatty liver disease, leading to liver dysfunction and jaundice.
Symptoms:
- Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes: The hallmark sign of jaundice.
- Dark Urine: Bilirubin is excreted in the urine, causing it to turn dark.
- Pale Stools: Lack of bile in the intestines can result in pale, clay-colored stools.
- Itching: Excess bilirubin in the skin may cause itching.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak is common in people with jaundice due to underlying liver or blood disorders.
- Abdominal Pain: Pain, especially in the upper right quadrant, may indicate liver or gallbladder problems.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive disturbances are common, particularly if bile flow is obstructed.
Prevention:
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B, which can lead to liver inflammation and jaundice.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake to reduce the risk of liver disease.
- Safe Food and Water: Avoid contaminated food and water, especially in areas with poor sanitation, to prevent hepatitis A.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing the risk of fatty liver disease can help prevent liver-related jaundice.
- Use Clean Needles: Avoid sharing needles to reduce the risk of hepatitis B and C.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Practicing safe sex reduces the risk of hepatitis infection.
Diagnosis:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure bilirubin levels and assess liver function. They also help identify specific causes like infections or blood disorders.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs can identify blockages in the bile ducts, gallbladder, or liver.
- Liver Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue may be taken to assess liver disease or damage.
- Urine Tests: Urine tests can measure bilirubin and other markers of liver function.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A specialized test to examine the bile ducts for obstructions.
Home Remedies:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support liver function and help flush out excess bilirubin.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that may support liver health. Add turmeric to your diet with caution.
- Sugarcane Juice: Known in traditional medicine to support liver function and aid digestion.
- Lemon Juice: Lemon helps detoxify the liver. Drinking warm lemon water may improve liver health.
- Papaya Leaves: Extracts of papaya leaves are believed to support liver function and reduce symptoms of jaundice.
- Bitter Gourd: Bitter gourd juice is used in some cultures to aid liver function and combat jaundice.
Treatment:
- Addressing Underlying Cause: Treatment depends on the underlying cause of jaundice (e.g., treating liver disease, removing gallstones, managing infections).
- Medications:
- Antivirals or Antibiotics: For hepatitis or infections causing jaundice.
- Corticosteroids: For autoimmune conditions affecting the liver.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: Surgery or endoscopic procedures may be necessary to remove blockages like gallstones or tumors.
- Blood Transfusions: For conditions like hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed too quickly.
- Phototherapy (for newborns): Newborn jaundice is often treated with phototherapy, which helps break down bilirubin in the skin.
Precautions:
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can further harm the liver and worsen jaundice.
- Avoid Hepatotoxic Medications: Certain medications may exacerbate liver damage, so they should be avoided unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Prevent infections like hepatitis by practicing good hygiene, especially in areas with poor sanitation.
- Follow Doctor’s Advice: If jaundice is related to a chronic condition, follow the treatment plan advised by your healthcare provider.
- Monitor Symptoms: If jaundice worsens or new symptoms develop (such as fever, pain, or confusion), seek medical care immediately.
Self-Care:
- Rest: Give your body time to heal, especially if liver function is impaired.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to support liver health. Avoid fatty, fried, or processed foods.
- Avoid Stress on the Liver: Avoid toxins, drugs, and alcohol that can damage the liver further.
- Manage Weight: Keep a healthy weight through diet and regular physical activity to reduce liver strain.
- Monitor Hydration: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, especially if you have jaundice due to liver problems.
Disclaimer:
Jaundice is a symptom of an underlying condition, often involving the liver, gallbladder, or blood. While home remedies and self-care measures may help relieve symptoms, they do not address the root cause. Always seek medical attention if you develop jaundice, as early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing serious complications. Follow your healthcare provider’s guidance for the appropriate tests and treatments. Delaying medical care can lead to severe liver damage or other complications.